Finfish Capture Techniques
Longlining
Trawling or Dragging
Seining
Gillnetting
Trapping
Hook and Lining
Longlining:
Midwater Longlining
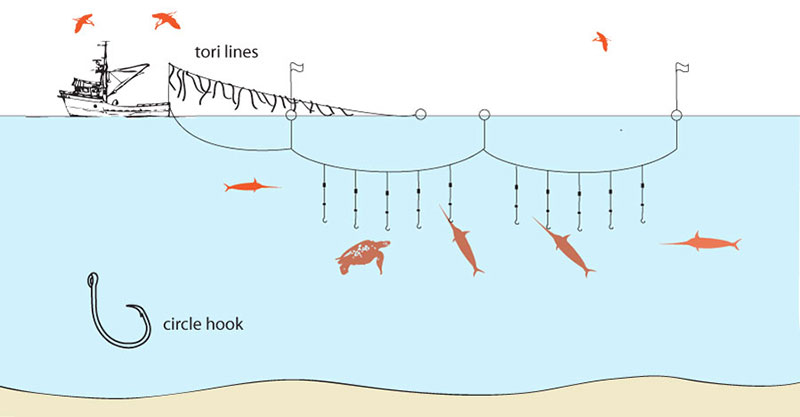
Longlining uses baited hooks, on offshoots of a single main line, to catch fish at any depth. The line can be anchored in areas too rough for trawling, or set adrift, suspended by floats.
Pelagic, or midwater, longline hooks are baited to attract fish such as swordfish, tuna and opah. Unfortunately they also catch sea life such as turtles, sea mammals and birds. Lines can be altered to mitigate bycatch by utilizing: circle hooks that are shaped so the hook won't set in a turtle's mouth, colored bait, weights to sink the bait faster, targeted locationing, and tori lines that scare away sea-birds.
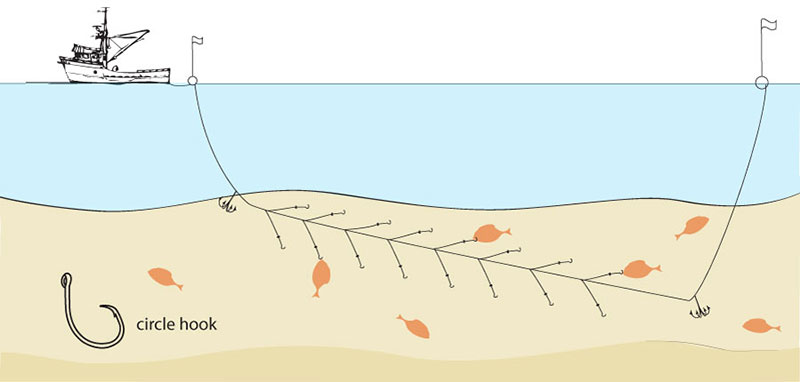
Bottom Longlining
Demersal, or bottom, longlining is a much more environmentally sound means of catching fish like halibut and true cod, which dwell on the ocean floor, than the very destructive alternatives of bottom trawling or dredging. Circle hooks are employed to ameliorate sea turtle deaths.
Trawling or Dragging:
Midwater Trawling
Trawling or Dragging is the method of fishing responsible for the greatest percentage of fishery landings. Trawling is simply described as towing a net through water.
Mid-water trawlers tow a funnel-shaped net through the water column between the surface and the bottom, targeting mid-level pelagic fish, such as true cod and pollock, resulting in less impact on fishery habitat and less bycatch.
Sandy & Muddy Soft Bottom Trawling
Sandy and Muddy, or Soft Bottom Trawling has less impact on the ocean floor because these environments and the species that live in them, such as Petrale Sole and Sand Dabs, are adaptable to periodic shifting caused by storms and currents. Scale, targeting skill, and equipment are factors that determine whether this method of capture is a sustainable one or not.
Rocky Bottom Trawling
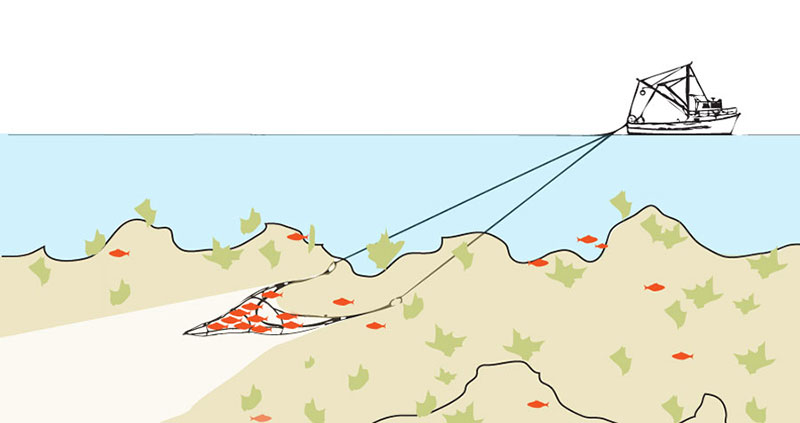
Rocky Bottom Trawling or Dragging is the method of fishing responsible for the greatest environmental damage.
This trawling drags a net weighted down with extremely heavy cables and rollers over the ocean floor, scraping everything in its path, including all sea creatures and plant life-forms, as well as the habitat necessary for their survival.
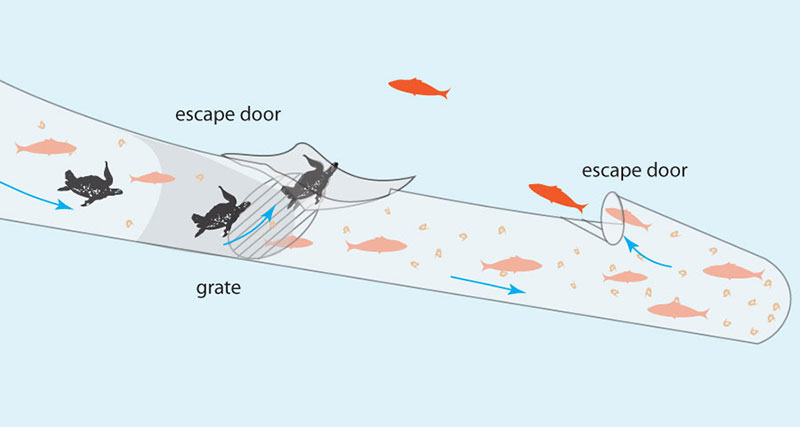
Turtle Extruder Devices (teds)
Turtle extruder devices, or (T.E.D.s) are Shrimp Trawler net modifications, consisting of grates that are sewn into nets adjacent to open flaps that function as escape hatches.
A) Sea Turtles and large fish carried by the current into the nets swim or float onto the grate through which they cannot fit.
B) The current gently forces the turtles up the grate and out the escape hatch.
C) Targeted shrimp fit through the grate and remain in the net while the turtles and larger fish swim free.
Bycatch Reduction Devices (birds)
A bycatch reduction device is an opening in a shrimp trawl net that allows finfish or other sea animals to escape, while the target species of shrimp is directed towards the bag end of the net.
BRDs are required in shrimp trawl nets in federal waters of the Gulf of Mexico and South Atlantic regions.
Seining:
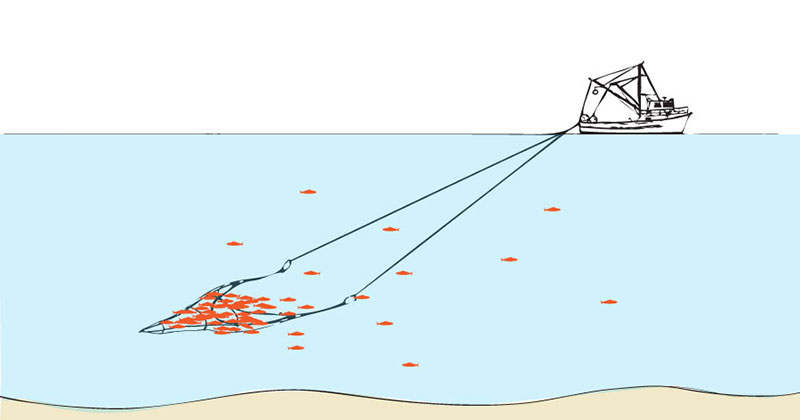
Purse Seining
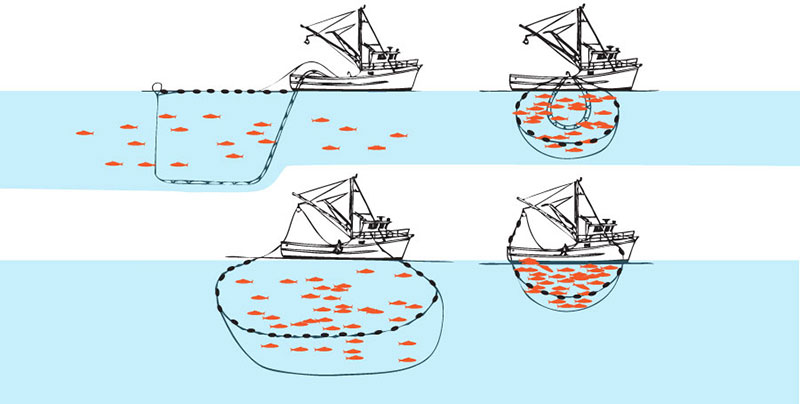
Purse seines are walls of netting used to encircle entire schools of fish such as sardines, mackerel, squid, and some tuna, at or near the surface. A drawstring cable is threaded through the bottom of the net. When the cable has pulled the netting tight, enclosing the fish in a pouch, the catch is hauled onboard with a dip net in a process called brailing.
A) A net with weights and buoys is laid out, forming a screen of net around the catch.
B) The drawstring cable at the weighted bottom of the net is cinched, or drawn in, closing the bottom.
C) The catch and the gear is drawn toward the boat.
D) Once the fish is concentrated in the purse, smaller meshed nets called brailers or fish pumps transport the fish from the seine to the boat.
Danish and Scottish Seining
Danish and Scottish seines are nets and lines used to catch species of ground fish, like sand dabs, sole, flounder and cod. Unlike trawling, which uses heavy cables, doors and trawls, Danish and Scottish seining use nets and lines spread out in a diamond shape along the sandy bottom of the ocean floor. The fish are herded into the path of the net by the lines, which gently stir up a mud cloud. Danish Seining keeps the boat in a fixed position and the gear is hauled along the bottom to get it back to the boat.
Scottish Seining tows the net and ropes along the ocean floor slowly, just enough to close the nets and bring the gear up to the boat, a method called "fly-dragging".
A) With a buoy on one end, nearly a mile of line and a light net are laid out from a boat that circles back to the buoy. The gear is lightweight, and used on smooth, sandy bottoms.
B) The circle of line and net is completed and the lines and nets fall to the bottom and gently settle. The boat slowly proceeds ahead, towing and pulling in the gear and catch, as the fish are herded into the net.
C) This slow, gentle method of pulling the gear and catch back to the vessel leaves dramatically less bottom degradation than trawling. It results in very low levels of bycatch, and nets are configured to result in less drag and more efficient fuel use.
Gillnetting:
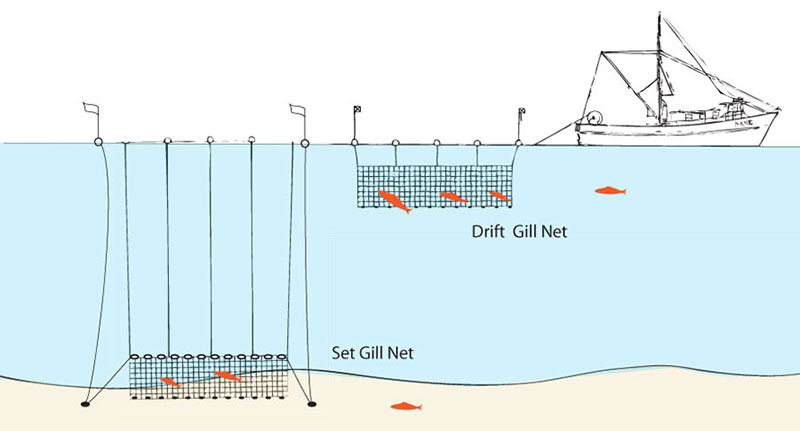
Open Ocean Gillnetting
Gillnetting and driftnetting, passive methods, can be used to harvest bottom or pelagic fish.
A gillnet is a wall of netting set in a straight line, equipped with weights at the bottom and floats at the top, and is usually anchored at each end. Fish such as swordfish, thresher shark, and rockfish try to swim through the net and are caught when their gill covers are snagged, hence the name gillnetting.
If allowed to drift freely, the method is referred to as driftnetting, and the method is more active.
River Gillnetting
Gillnetting is used in rivers to target specific species swimming in specific rivers such as spawning salmon, and sturgeon.
Trapping:
Weirs
Weirs are constructions designed from branches or stones that impede free movement of fish such as mackerel and herring by obstructing running waters, and then guiding fish into cordoned areas as they migrate.
Fish Traps
Fish traps are large net or link traps suspended in the water or on the bottom, marked by buoys, weighted, and anchored. Fish are able to swim in, small size fish can escape and non-targeted fish can be released alive when the fishermen return to harvest the targeted fish.
Hook & Lining:
Jigging
Jigging is the setting of a line, with baited hooks or lures, that is continually jerked. The motion, achieved by hand or with a jigging machine, induces fish such as cod and squid, to take the hook.
Harpooning
Harpooning is used to catch large, near surface swimming fish, and is a very targeted method, without bycatch. Harpoon fishermen spear large pelagic fish, such as swordfish, with wooden or aluminum shafted javelin-like hooks attached to buoyed lines. The fish is caught and hauled onto the boat.
Rod & Reel and Handlining
These methods involve a hand line or rod-and-reel, sometimes with more than one hook, that is literally pulled in by hand. There are no engine devices aiding in these techniques of fish retrieval. Rockfish, cod and ling cod are often caught using this method.
Trolling
Trolling is simply a moving hook and line towed as single fishing lines behind a moving boat. Salmon, ono and mahi mahi are often caught using this method.
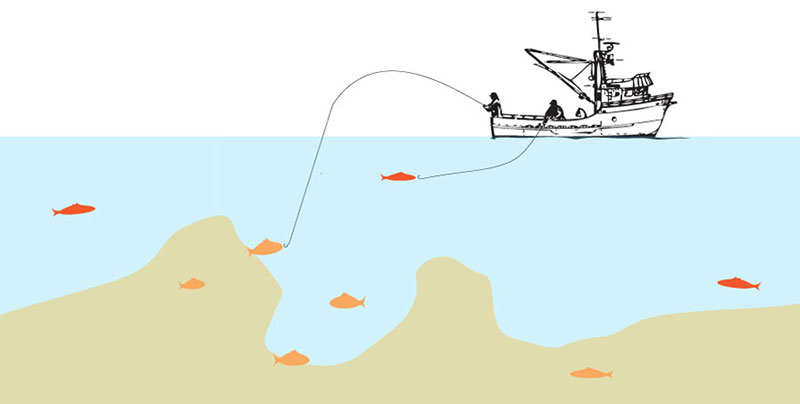
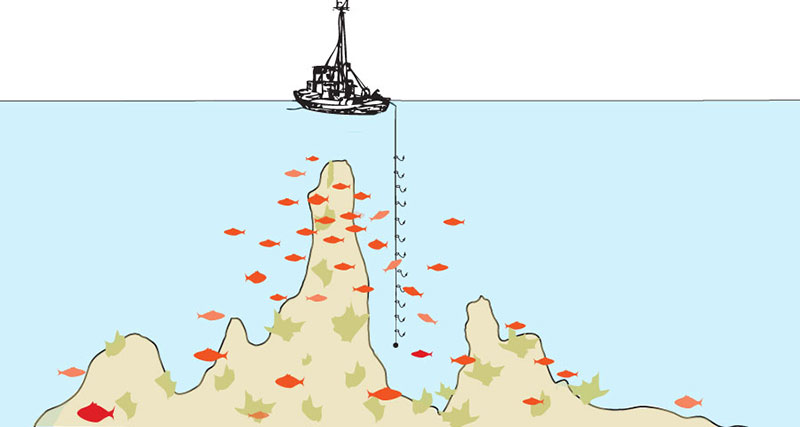
Vertical Hook & Line
A multi-hooked line weighted at the bottom is dropped into the waters adjacent to vertical outcroppings where fish congregate. The fisherman gently drifts into position and holds that position while slowly retracting the line, encouraging fish, then, in succession, other fish, to bite onto it.
This method of capture is used by small boat artisanal fishermen and demands a high level of skill and knowledge. Accepted by experts as one of the cleanest and most target-specific fishing methods, with no environmental damage, hook and line fishing is fast becoming a lost art. Newly legislated governmental permit and quota restrictions that allow commercial trawlers rights to waters, prohibit hook & line fishermen access to the areas that they've been stewarding and sustainably harvesting from for years.